UPDATE: The second part is now available: How to test LINQ and mappings.
There are countless articles on the web about unit tests: TDD approach, beginner's guides, mocking frameworks, test coverage tools and more. However, the vast majority of these articles are either too "Hello World"-like or focus more on tools, while missing the key point — how to write unit tests that are useful and deliver the most value. In this article I'll share some best practices, which I believe will get your unit tests to the next level.
This is an example-driven article inasmuch as, in my view, this is the best way to explain things in programming. We're going to start with a code example (a C# class plus a few unit tests for this class) and highlight some important points related to what we want to test and how we're going to do that. Then we'll review one of the many ways (my favorite one) to structure unit tests. Finally, I'll share a few awesome libraries that I use in all my test projects.
Ready? Lets' get started🍿
Example 1
UserManager
public class UserManager : IUserManager
{
private readonly IUserRepository _userRepository;
private readonly IUserGuard _userGuard;
public UserManager(IUserRepository userRepository, IUserGuard userGuard)
{
_userRepository = userRepository;
_userGuard = userGuard;
}
public async Task ChangeEmail(int userId, string newEmail, CancellationToken ct = default)
{
var user = await _repository.GetUser(userId, ct);
_guard.UserExists(user);
_guard.UserIsAllowedToChangeEmail(user!);
_guard.EmailIsValid(newEmail);
_guard.EmailIsNew(user!, newEmail);
user!.Email = newEmail;
await _repository.Save(user, ct);
}
}
Test strategy
We want to verify that all calls to
IUserGuardhappen in the correct order, and, most importantly, come before_repository.Save. In other words, validation has to go before the data is saved to the database.Make sure we pass correct parameters to all methods that we call here.
Our
ChangeEmailmethod actually calls_repository.Save.We save the
userobject with the new email address.
Tests
public class UserManagerTests
{
public class ChangeEmail : UserManagerTestsBase
{
[Theory]
[AutoData]
public async Task Should_change_email(int userId,
string newEmail,
User user,
CancellationToken ct)
{
//! Arrange
Repository.GetUser(userId, ct).Returns(user);
//! Act
await Manager.ChangeEmail(userId, newEmail, ct);
//! Assert
Received.InOrder(() =>
{
Guard.Received(1).UserExists(user);
Guard.Received(1).UserIsAllowedToChangeEmail(user);
Guard.Received(1).EmailIsValid(newEmail);
Guard.Received(1).EmailIsNew(user, newEmail);
Repository.Received(1).Save(Arg.Is<User>(x => x == user &&
x.Email == newEmail),
ct);
});
}
}
public abstract class UserManagerTestsBase
{
protected readonly UserManager Manager;
protected readonly IUserRepository Repository;
protected readonly IUserGuard Guard;
protected UserManagerTestsBase()
{
Repository = Substitute.For<IUserRepository>();
Guard = Substitute.For<IUserGuard>();
Manager = new UserManager(Repository, Guard);
}
}
}
Notes
Instead of hardcoding test data, we generated random values using
[AutoData](AutoFixture.Xunit2 library).To validate the order of method calls we used
Received.InOrder(...)(NSubstitute — the best mocking library for .NET).We used
Arg.Is<User>(x => x.Email == newEmail)in order to make sure we change email address of theuserbefore saving this object to the database.
Now we're going to add one more method to the UserManager class and unit test it.
Example 2
public class UserManager : IUserManager
{
private readonly IUserRepository _repository;
private readonly IUserGuard _guard;
public UserManager(IUserRepository repository, IUserGuard guard)
{
_repository = repository;
_guard = guard;
}
// public async Task ChangeEmail(int userId, string newEmail, CancellationToken ct = default)
// {...}
public async Task ChangePassword(int userId, string newPassword, CancellationToken ct = default)
{
var user = await _repository.GetUser(userId, ct);
if (user == null)
{
throw new ApplicationException($"User {userId} not found");
}
user.Password = newPassword;
await _repository.Save(user, ct);
}
}
Test strategy
This method has an
ifstatement, so we want to make sure that correct branch of code runs depending on the condition in theifstatement.Instead of ignoring the exception, we want to validate the type of the thrown exception along with its message.
Same as in the previous example, we want to verify that we pass the
userobject with an updated password to the_repository.Savemethod.If an exception is thrown, then the
_repository.Savemethod must not get called.
Tests
public class UserManagerTests
{
// public class ChangeEmail : UserManagerTestsBase
// {...}
public class ChangePassword : UserManagerTestsBase
{
[Theory, AutoData]
public async Task Should_throw_ApplicationException_when_user_not_found(int userId,
string newPassword,
CancellationToken ct)
{
//! Act
var action = () => Manager.ChangePassword(userId, newPassword, ct);
//! Assert
await action.Should()
.ThrowAsync<ApplicationException>()
.WithMessage($"User {userId} not found");
await Repository.DidNotReceiveWithAnyArgs().Save(Arg.Any<User>(), Arg.Any<CancellationToken>());
}
[Theory, AutoData]
public async Task Should_change_password_and_save(int userId,
string newPassword,
User user,
CancellationToken ct)
{
//! Arrange
Repository.GetUser(userId, ct).Returns(user);
//! Act
await Manager.ChangePassword(userId, newPassword, ct);
//! Assert
await Repository.Received(1).Save(Arg.Is<User>(x => x == user &&
x.Password == newPassword),
ct);
}
}
public abstract class UserManagerTestsBase
{
protected readonly UserManager Manager;
protected readonly IUserRepository Repository;
protected readonly IUserGuard Guard;
protected UserManagerTestsBase()
{
Repository = Substitute.For<IUserRepository>();
Guard = Substitute.For<IUserGuard>();
Manager = new UserManager(Repository, Guard);
}
}
}
Notes
For the
ChangePasswordmethod we have two tests: first test to validate that an exception gets thrown when a user not found, and the second one to check that we make a call to_repository.Save.Note how we test exceptions: instead of try-catch we create a delegate to the test method and then do
action.Should().ThrowAsync<ApplicationException>().
Our tests are done, now let's take a look at the unit tests coverage in order to make sure we didn't miss anything and there is no not tested code left.
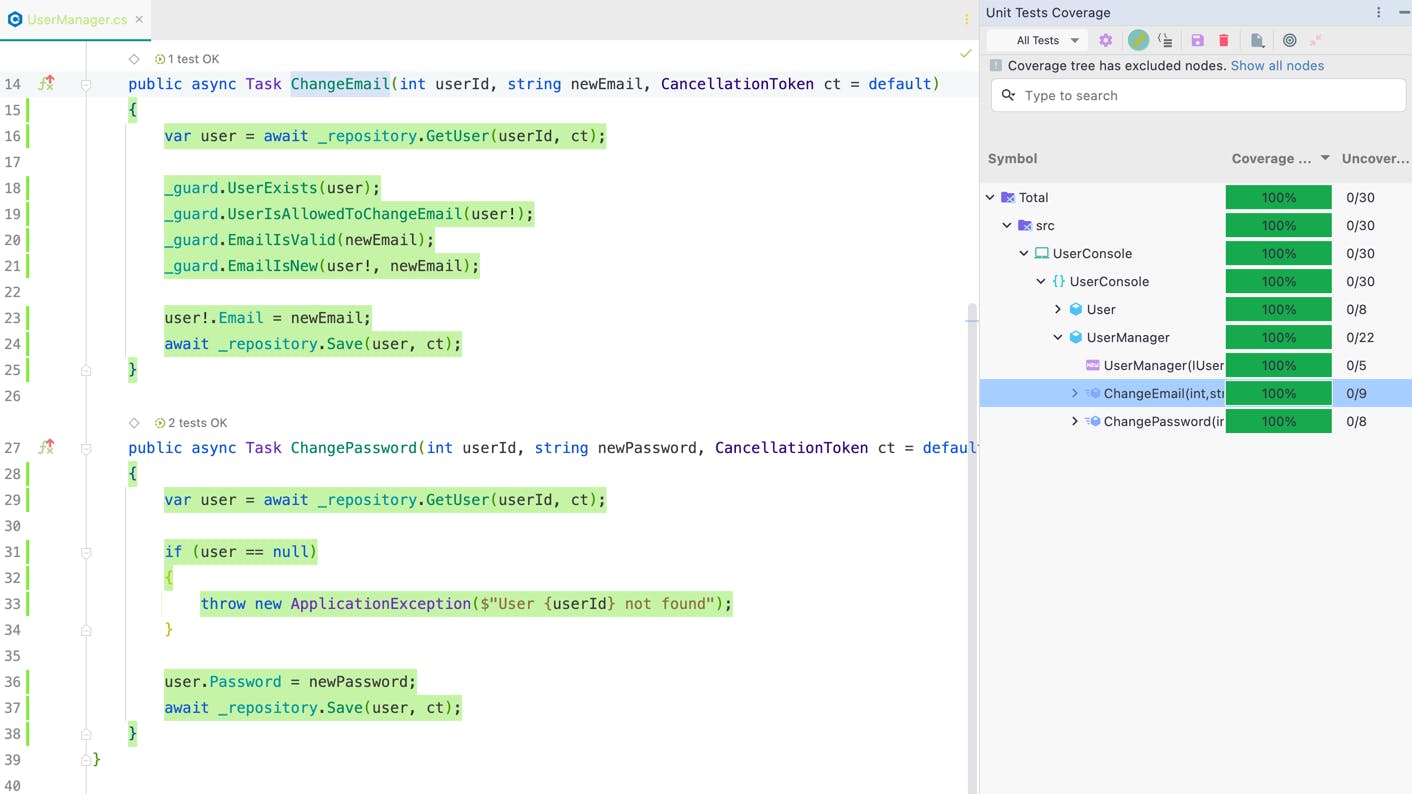
Tests Structure
To a large extent, the layout of a test project is a matter of taste. Here is the way I prefer to do this. For classes with more than one method (managers, services etc) the structure of the related class with unit tests would be as follows (Gist on GitHub):
public class MyClassTests
{
public class Method1 : MyClassTestsBase
{
[Theory]
[AutoData]
public async Task Should_return_A_when_X(parameters)
{
//! Arrange
// ...
//! Act
// ...
//! Assert
// ...
}
[Theory]
[AutoData]
public async Task Should_throw_B_when_Y(parameters)
{
//! Arrange
// ...
//! Act
// ...
//! Assert
// ...
}
}
public class Method2 : MyClassTestsBase
{
[Fact]
public async Task Should_return_A_when_X()
{
//! Arrange
// ...
//! Act
// ...
//! Assert
// ...
}
[Fact]
public async Task Should_throw_B_when_Y()
{
//! Arrange
// ...
//! Act
// ...
//! Assert
// ...
}
}
public abstract class MyClassTestsBase
{
protected readonly MyClass Instance;
protected readonly IDependency1 Dependency1;
protected readonly IDependency2 Dependency2;
protected UserManagerTestsBase()
{
Dependency1 = Substitute.For<IDependency1>();
Dependency2 = Substitute.For<IDependency2>();
Instance = new MyClass(IDependency1, IDependency2);
}
}
}
This is what it looks like in the test runner:

Unit tests structure for classes with a single method (message handlers, factories etc):
public class MyHandlerTests
{
private readonly MyHandler _handler;
public MyHandlerTests()
{
_handler = new MyHandler();
}
[Fact]
public void Should_do_A_when_X()
{
//! Arrange
//! Act
//! Assert
}
}
Alright, so we have an understanding of the key concepts of unit testing and learned the best way to structure our tests. Now let's check out a few brilliant libraries which, I'm absolutely sure, you'll love.
Libraries and frameworks
xUnit
It’s usually a choice between xUnit, nUnit and MSTest, and my personal preference goes to the former. A while ago when Microsoft started using xUnit in its projects, this framework became a default option.
Autofixture Cheat Sheet
Instead of using hard coded values for tests, Autofixture can generate random data for us.
var fixture = new Fixture();
var firstName = fixture.Create<string>();
var numOfUsers = fixture.Create<int>();
var employees = fixture.CreateMany<Employee>();
Autofixture.Xunit2 nuget for [AutoData] attribute (the one we used in our examples).
NSubstitute
There are a few mocking libraries out there, but I find this one the most explicit, natural and clean. A small bonus: NSubstitute.Analyzers — Roslyn analyzers to detect (during compilation) possible errors using NSubstitute.
FluentAssertions
Fantastic assertion framework with a very detailed and well-structured documentation.
A couple of examples taken from their docs:
string actual = "ABCDEFGHI";
actual.Should().StartWith("AB").And.EndWith("HI").And.Contain("EF").And.HaveLength(9);
IEnumerable<int> numbers = new[] { 1, 2, 3 };
numbers.Should().OnlyContain(n => n > 0);
numbers.Should().HaveCount(4, "because we thought we put four items in the collection");
Isn't it beautiful?
Stryker.NET
Stryker offers mutation testing for your .NET Core and .NET Framework projects. It allows you to test your tests by temporarily inserting bugs in your source code.
It's a very interesting tool which modifies the source code and expects tests to fail. If they don't, it complains about incomplete unit tests or poor tests coverage.
Summary
We've analyzed two simple, yet important code examples that cover the most popular scenarios of unit testing. Learned one of the ways to structure and group tests, and made a list of essential libraries that will make your tests clean, explicit and more effective.
UPDATE: The second part is now available: How to test LINQ and mappings.
Cheers!

